









This easy-to-grow fruiting tree will flower and fruit once it reaches a height of 1 1/2-2', often within the first year. Small clusters of lilac-colored flowers bloom intermittently year-rounbd
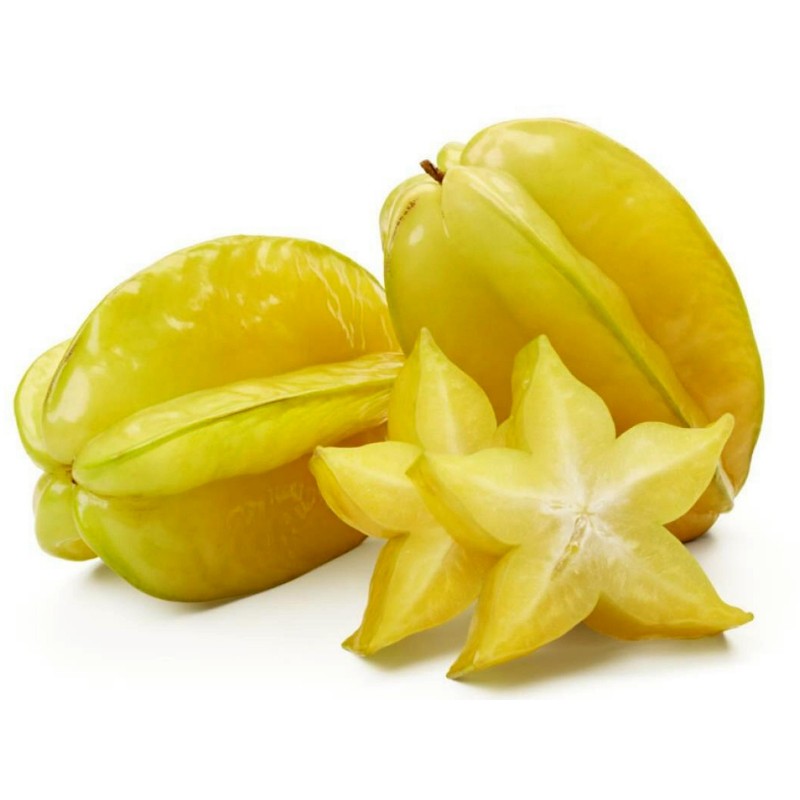
Carambola, also known as star fruit, is the fruit of Averrhoa carambola, a species of tree native to tropical Southeast Asia. The fruit is commonly consumed throughout Southeast Asia, the South Pacific, Micronesia, parts of East Asia, and the Caribbean. The tree is cultivated throughout tropical areas of the world.
The fruit has distinctive ridges running down its sides (usually 5–6). When cut in cross-section, it resembles a star, giving its name as star fruit. The entire fruit is edible, usually raw, and may be cooked or made into relishes, preserves, garnish, and juices.

The center of diversity and the original range of Averrhoa carambola is tropical Southeast Asia, where it has been cultivated over centuries.[1][3][4][5] It was introduced to the Indian Subcontinent and Sri Lanka by Austronesian traders, along with ancient Austronesian cultigens like coconuts, langsat, noni, and santol.[6] They remain common in those areas and in East Asia and throughout Oceania and the Pacific Islands.[1][2] They are cultivated commercially in India, Southeast Asia, southern China, Taiwan, and the southern United States. They are also grown in Central America, South America, the Southwestern United States and Florida, the Caribbean, and parts of Africa.[1][2] They are grown as ornamentals.[1] Carambola is considered to be at risk of becoming an invasive species in many world regions.
The carambola tree has a short trunk with many branches, reaching up to 30 feet (9.1 m) in height.[1] Its deciduous leaves are 6–10 inches (15–25 cm) long, with 5 to 11 ovate leaflets medium-green in color.[1] Flowers are lilac in color, with purple streaks, and are about 0.25 inches (6.4 mm) wide.
The showy fruits have a thin, waxy pericarp, orange-yellow skin, and crisp, yellow flesh with juice when ripe.[1] The fruit is about 5 to 15 centimetres (2 to 6 inches) in length and is an oval shape. It usually has five or six prominent longitudinal ridges.[1] In cross section, it resembles a star.[1][2] The flesh is translucent and light yellow to yellow in color. Each fruit can have 10 to 12 flat light brown seeds about 6 to 13 mm (0.25 to 0.5 in) in width and enclosed in gelatinous aril. Once removed from the fruit, they lose viability within a few days.[7][8][9]
Like the closely related bilimbi, there are two main types of carambola: the small sour (or tart) type and the larger sweet type. The sour varieties have a higher oxalic acid content than the sweet type. A number of cultivars have been developed in recent years. The most common cultivars grown commercially include the sweet types "Arkin" (Florida), "Yang Tao" (Taiwan), "Ma fueng" (Thailand), "Maha" (Malaysia), and "Demak" (Indonesia) and the sour types "Golden Star", "Newcomb", "Star King", and "Thayer" (all from Florida). Some of the sour varieties like "Golden Star" can become sweet if allowed to ripen.
Carambola is known by many names across its regions of cultivation, including balimbing in Southeast Asia, ma fen in China, kamaranga in India, and carambolo in Spanish-speaking countries, as examples.[1][2]

| Nutritional value per 100 g (3.5 oz) | |
|---|---|
| Energy | 128 kJ (31 kcal) |
|
Carbohydrates
|
6.73 g
|
| Sugars | 3.98 g |
| Dietary fiber | 2.8 g |
|
Fat
|
0.33 g
|
|
Protein
|
1.04 g
|
| Vitamins | Quantity%DV† |
| Vitamin A equiv.
lutein zeaxanthin
|
66 μg
|
| Thiamine (B1) |
1%
0.014 mg |
| Riboflavin (B2) |
1%
0.016 mg |
| Niacin (B3) |
2%
0.367 mg |
| Pantothenic acid (B5) |
8%
0.391 mg |
| Vitamin B6 |
1%
0.017 mg |
| Folate (B9) |
3%
12 μg |
| Choline |
2%
7.6 mg |
| Vitamin C |
41%
34.4 mg |
| Vitamin E |
1%
0.15 mg |
| Minerals | Quantity%DV† |
| Calcium |
0%
3 mg |
| Iron |
1%
0.08 mg |
| Magnesium |
3%
10 mg |
| Manganese |
2%
0.037 mg |
| Phosphorus |
2%
12 mg |
| Potassium |
3%
133 mg |
| Sodium |
0%
2 mg |
| Zinc |
1%
0.12 mg |
| Other constituents | Quantity |
| Water | 91.4 g |
Link to USDA Database entry
|
|
|
|
| †Percentages are roughly approximated using US recommendations for adults. Source: USDA Nutrient Database |
|
The entire fruit is edible, including the slightly waxy skin. The flesh is crunchy, firm, and extremely juicy.[2] It does not contain fibers and has a texture similar in consistency to that of grapes. Carambolas are best consumed shortly after they ripen, when they are yellow with a light shade of green or just after all traces of green have disappeared. They will also have brown ridges at the edges and feel firm. Fruits picked while still slightly green will turn yellow in storage at room temperature, but will not increase in sugar content. Overripe carambola will be yellow with brown spots and can become blander in taste and soggier in consistency.
Ripe sweet type carambolas are sweet without being overwhelming as they rarely have more than 4% sugar content. They have a tart, sour undertone, and an oxalic acid odor. The taste is difficult to match, but it has been compared to a mix of apple, pear, grape, and citrus family fruits. Unripe star fruits are firmer and sour, and taste like green apples.
Ripe carambolas may also be used in cooking. In Southeast Asia, they are usually stewed in cloves and sugar, sometimes with apples. In China, they are cooked with fish. In Australia, they may be cooked as a vegetable, pickled, or made into jams. In Jamaica they are sometimes dried.
Unripe and sour type carambolas can be mixed with other chopped spices to make relishes in Australia.[1] In the Philippines, unripe carambolas are eaten dipped in rock salt. In Thailand, they are cooked together with shrimp.[1]
The juice from carambolas is also used in iced drinks, particularly the juice of the sour varieties. In the Philippines they can be used as seasoning. In India, the juice is bottled for drinking.
Raw carambola is 91% water, 7% carbohydrates, 1% protein, and has negligible fat (table). A 100 gram reference amount of raw fruit supplies 31 calories and a rich content of vitamin C (41% of the Daily Value), with no other micronutrients in significant content (table).
Carambolas contain caramboxin[13] and oxalic acid.[1][14] Both substances are harmful to individuals suffering from kidney failure, kidney stones, or those under kidney dialysis treatment.[14] Consumption by those with kidney failure can produce hiccups, vomiting, nausea, mental confusion, and sometimes death.[15][16][17] Caramboxin is a neurotoxin which is structurally similar to phenylalanine, and is a glutamatergic agonist.[13]
Like the grapefruit, carambola is considered to be a potent inhibitor of seven cytochrome P450 isoforms.[18][19] These enzymes are significant in the first-pass elimination of many medications, and, thus, the consumption of carambola or its juice in combination with certain prescription medications can significantly increase their effective dosage within the body.


The carambola is a tropical and subtropical fruit which can be grown at elevations up to 1,200 metres (4,000 feet). It prefers full sun exposure, but requires enough humidity and annual rainfall of at least 1,800 mm (70 in).[1][2] It does not have a soil type preference, but will thrive in loam and requires good drainage.[1] Moderate irrigation supports its growth during dry seasons.[1] Heavy rains may inhibit fruit production.[1]
Carambola trees are planted at least 6 m (20 ft) from each other and typically are fertilized three times a year. The tree grows rapidly and typically produces fruit at four or five years of age. The large amount of rain during spring actually reduces the amount of fruit, but, in ideal conditions, carambola can produce from 90 to 180 kilograms (200 to 400 pounds) of fruit a year. The carambola tree flowers throughout the year, with main fruiting seasons from April to June and October to December in Malaysia,[20] for example, but fruiting also occurs at other times in some other locales, such as South Florida.[1][8]
Growth and leaf responses of container-grown `Arkin' carambola (Averrhoa carambola L.) trees to long-term exposure of 25%, 50%, or 100% sunlight showed that shading increased rachis length and leaflet area, decreased leaflet thickness, and produced more horizontal branch orientation.[21]
Major pests are carambola fruit flies, fruit moths, ants, and birds.[1][7][20] Crops are also susceptible to frost.[7]
Top producers of carambola in the world market include Australia, Guyana, India, Israel, Malaysia, the Philippines, Taiwan, and the United States.[8] Malaysia is a global leader in star fruit production by volume and ships the product widely to Asia and Europe.[20] Due to concerns over pests and pathogens, however, whole star fruits cannot yet be imported to the US from Malaysia under current United States Department of Agriculture regulations. In the United States, carambolas are grown in tropical and semitropical areas, including Texas, South Carolina, Louisiana, California, Virginia, Florida and Hawaii.[1][22]
In the United States, commercial cultivation and broad consumer acceptance of the fruit only dates to the 1970s, attributable to Morris Arkin, a backyard horticulturalist, in Coral Gables, Florida. The 'Arkin' variety represented 98% of the acreage in South Florida in the early 21st century.[23]
The trees are also grown as ornamentals for their abundant brightly colored and unusually shaped fruits, as well as for their attractive dark green leaves and their lavender to pink flowers.[8]
Like the bilimbi, the juice of the more acidic sour types can be used to clean rusty or tarnished metal (especially brass) as well as bleach rust stains from cloth. They may also be used as a mordant in dyeing.
Fisa tehnica
 Reviews (0)
Reviews (0)