Seeds Gallery Com,
5/
5
<p>The<span> </span><b>Scoville scale</b><span> </span>is a<span> </span>measurement<span> </span>of the<span> </span>pungency<span> </span>(spiciness or "heat") of<span> </span>chili peppers<span> </span>and other spicy foods, as recorded in Scoville Heat Units (SHU) based on the concentration of<span> </span>capsaicinoids, among which<span> </span>capsaicin<span> </span>is the predominant component.<span> </span>The scale is named after its creator, American pharmacist<span> </span>Wilbur Scoville, whose 1912 method is known as the Scoville<span> </span>organoleptic<span> </span>test.<span> </span>The Scoville organoleptic test is the most practical method for estimating SHU and is a subjective assessment derived from the capsaicinoid sensitivity by people experienced with eating hot chilis.</p>
<p>An alternative method, using<span> </span>high-performance liquid chromatography<span> </span>(HPLC) can be used to analytically quantify the capsaicinoid content as an indicator of pungency.<span> </span>As of 2011, the subjective organoleptic test has been largely superceded by analytical methods such as chromatography.</p>
<h2><span class="mw-headline" id="Scoville_organoleptic_test">Scoville organoleptic test</span></h2>
<p>In the Scoville organoleptic test, an exact weight of dried pepper is dissolved in alcohol to extract the heat components (capsaicinoids), then diluted in a solution of sugar water.<sup id="cite_ref-twi_3-4" class="reference">[3]</sup><sup id="cite_ref-Peter2012_10-0" class="reference">[10]</sup><sup id="cite_ref-tainter_11-0" class="reference">[11]</sup><span> </span>Decreasing concentrations of the extracted capsaicinoids are given to a panel of five trained tasters, until a majority (at least three) can no longer detect the heat in a dilution.<sup id="cite_ref-five38_1-1" class="reference">[1]</sup><sup id="cite_ref-twi_3-5" class="reference">[3]</sup><sup id="cite_ref-Peter2012_10-1" class="reference">[10]</sup><sup id="cite_ref-tainter_11-1" class="reference">[11]</sup><span> </span>The heat level is based on this dilution, rated in multiples of 100 SHU.<sup id="cite_ref-Peter2012_10-2" class="reference">[10]</sup></p>
<p>Another source using<span> </span>subjective assessment<span> </span>stated: "Conventional methods used in determining the level of pungency or capsaicin concentration are using a panel of tasters (Scoville Organoleptic test method). ... Pepper pungency is measured in Scoville Heat Units (SHU). This measurement is the highest dilution of a chili pepper extract at which heat can be detected by a taste panel."<sup id="cite_ref-guzman_4-2" class="reference">[4]</sup><sup id="cite_ref-12" class="reference">[12]</sup></p>
<p>A weakness of the Scoville organoleptic test is its imprecision due to human subjectivity, depending on the taster's palate and number of mouth heat<span> </span>receptors, which vary widely among people.<sup id="cite_ref-five38_1-2" class="reference">[1]</sup><sup id="cite_ref-guzman_4-3" class="reference">[4]</sup><span> </span>Another weakness is<span> </span>sensory fatigue;<sup id="cite_ref-five38_1-3" class="reference">[1]</sup><span> </span>the palate is quickly desensitized to capsaicinoids after tasting a few samples within a short time period.<sup id="cite_ref-Peter2012_10-3" class="reference">[10]</sup><span> </span>Results vary widely (up to ± 50%) between laboratories.<sup id="cite_ref-tainter_11-2" class="reference">[11]</sup></p>
<h2><span class="mw-headline" id="Pungency_units">Pungency units</span></h2>
<div class="thumb tright">
<div class="thumbinner"><img alt="" src="https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/3/38/Red_savina_cropped.jpg/220px-Red_savina_cropped.jpg" width="220" height="202" class="thumbimage" /><div class="thumbcaption">
<div class="magnify"></div>
The<span> </span>Red Savina pepper, a hot chili.<sup id="cite_ref-:3_13-0" class="reference">[13]</sup></div>
</div>
</div>
<p>Since the 1980s, spice heat has been assessed quantitatively by<span> </span>high-performance liquid chromatography<span> </span>(HPLC), which measures the concentration of heat-producing capsaicinoids, typically with capsaicin content as the main measure.<sup id="cite_ref-guzman_4-4" class="reference">[4]</sup><sup id="cite_ref-collins_5-2" class="reference">[5]</sup><span> </span>As stated in one review: "the most reliable, rapid, and efficient method to identify and quantify capsaicinoids is HPLC; the results of which can be converted to Scoville Heat Units by multiplying the parts-per-million by 16."<sup id="cite_ref-guzman_4-5" class="reference">[4]</sup><span> </span>HPLC results permit the measurement of a substance’s capsaicin capacity to produce perceived heat ("pungency"). This method gives results in<span> </span>American Spice Trade Association<span> </span>"pungency units", which are defined as one part capsaicin per million parts<span> </span>dried pepper mass.<sup id="cite_ref-collins_5-3" class="reference">[5]</sup></p>
<p>For<span> </span>parts per million<span> </span>(ppm) measurements, SHU units are calculated from "parts per million of heat" (ppmH), which is found with the following calculation:</p>
<p><span class="mwe-math-element"><img src="https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/851d90fcf2e4f5511e93e76868ab5f72c66e5acf" class="mwe-math-fallback-image-inline" alt="{displaystyle {text{ppmH}}={frac {{text{peak area}}({{text{capsaicin}})}+0.82cdot {text{peak area}}({text{dihydrocapsaicin)}}}{{text{peak area}}({text{standard)}}}}}" /></span></p>
<p>Peak areas are calculated from HPLC traces of dry samples of the substance to be tested in 1 ml of<span> </span>acetonitrile. The standard used to calibrate the calculation is 1 gram of capsaicin. Scoville heat units are found by multiplying the ppmH value by a factor of 15 or 16.<sup id="cite_ref-collins_5-5" class="reference"></sup></p>
<p>An orally administered capsule of capsaicinoids claiming 100,000 Scoville units will correspond to around 6.6 mg of capsaicinoids.</p>
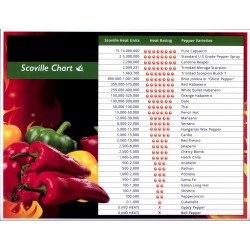
<p>The levels of pungency, in terms of Scoville units are:</p>
<table class="wikitable"><caption></caption>
<tbody><tr><th>Pungency</th>
<th>SHU</th>
</tr><tr><td>Very highly pungent</td>
<td>Above 80,000</td>
</tr><tr><td>Highly pungent</td>
<td>25,000 to 70,000</td>
</tr><tr><td>Moderately pungent</td>
<td>3,000 to 25,000</td>
</tr><tr><td>Mildly pungent</td>
<td>700 to 3,000</td>
</tr><tr><td>Non pungent</td>
<td>0 to 700</td>
</tr></tbody></table><p></p>
<h2><span class="mw-headline" id="Scoville_ratings">Scoville ratings</span></h2>
<h3><span class="mw-headline" id="Considerations">Considerations</span></h3>
<p>Since Scoville ratings are defined per unit of dry mass, comparison of ratings between products having different water content can be misleading. For example, typical fresh chili peppers have a water content around 90%, whereas<span> </span>Tabasco sauce<span> </span>has a water content of 95%.<sup id="cite_ref-15" class="reference">[15]</sup><span> </span>For law-enforcement-grade<span> </span>pepper spray, values from 500,000 up to 5 million SHU have been reported,<sup id="cite_ref-five38_1-4" class="reference">[1]</sup><sup id="cite_ref-16" class="reference">[16]</sup><span> </span>but the actual strength of the spray depends on the dilution.</p>
<p>Numerical results for any specimen vary depending on its cultivation conditions and the uncertainty of the laboratory methods used to assess the capsaicinoid content.<sup id="cite_ref-guzman_4-7" class="reference">[4]</sup><span> </span>Pungency values for any pepper are variable, owing to expected variation within a species, possibly by a factor of 10 or more, depending on<span> </span>seed lineage, climate and<span> </span>humidity, and soil composition supplying nutrients. The inaccuracies described in the measurement methods also contribute to the imprecision of these values.<sup id="cite_ref-guzman_4-8" class="reference">[4]</sup><sup id="cite_ref-tainter_11-3" class="reference">[11]</sup></p>
<h3><span class="mw-headline" id="Capsicum_peppers"><i>Capsicum</i><span> </span>peppers</span></h3>
<p><i>Capsicum</i><span> </span>chili peppers<span> </span>are commonly used to add pungency in<span> </span>cuisines<span> </span>worldwide.<sup id="cite_ref-twi_3-7" class="reference">[3]</sup><sup id="cite_ref-guzman_4-9" class="reference">[4]</sup><span> </span>The range of pepper heat reflected by a Scoville score is from 100 or less (sweet peppers) to over 3 million (Pepper X) (table below; Scoville scales for individual chili peppers are in the respective linked article).</p>
<table class="wikitable"><tbody><tr><th>Scoville heat units</th>
<th>Example peppers</th>
</tr><tr><td>800,000 to 3,200,000</td>
<td>Pepper X,<sup id="cite_ref-chili2_17-0" class="reference"></sup><span> </span>Carolina Reaper,<sup id="cite_ref-latimes_18-0" class="reference"></sup><span> </span>Dragon's Breath<sup id="cite_ref-CBS_19-0" class="reference"></sup></td>
</tr><tr><td>350,000 to 800,000</td>
<td>Red savina,<sup id="cite_ref-:3_13-1" class="reference"></sup><span> </span>Chocolate habanero<sup id="cite_ref-20" class="reference"></sup></td>
</tr><tr><td>100,000 to 350,000</td>
<td>Habanero,<span> </span>Scotch Bonnet<sup id="cite_ref-About_21-0" class="reference"></sup></td>
</tr><tr><td>10,000 to 100,000</td>
<td>Malagueta pepper,<span> </span>Cayenne pepper</td>
</tr><tr><td>1,000 to 10,000</td>
<td>Guajillo pepper,<span> </span>Jalapeño</td>
</tr><tr><td>100 to 1,000</td>
<td>Banana pepper,<span> </span>Cubanelle</td>
</tr><tr><td>0 to 100</td>
<td>Bell pepper,<span> </span>Pimento</td>
</tr></tbody></table><h3><span class="mw-headline" id="Capsaicinoids">Capsaicinoids</span></h3>
<div class="thumb tright">
<div class="thumbinner"><img alt="" src="https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/ad/Capsaicin_pharmacophore.svg/350px-Capsaicin_pharmacophore.svg.png" width="350" height="230" class="thumbimage" /><div class="thumbcaption">
<div class="magnify"></div>
Capsaicin pharmacophore</div>
</div>
</div>
<p>The class of compounds causing pungency in plants like chili peppers is called<span> </span>capsaicinoids, which display a<span> </span>linear correlation<span> </span>between concentration and Scoville scale, and may vary in content during<span> </span>ripening.<sup id="cite_ref-22" class="reference">[22]</sup><span> </span>Capsaicin is the major capsaicinoid in chili peppers.<sup id="cite_ref-collins_5-6" class="reference">[5]</sup></p>
<table class="wikitable"><tbody><tr><th>Scoville heat units</th>
<th>Chemical</th>
<th>Ref</th>
</tr><tr><td>16,000,000,000</td>
<td>Resiniferatoxin</td>
<td><sup id="cite_ref-QUE_23-0" class="reference">[23]</sup></td>
</tr><tr><td>5,300,000,000</td>
<td>Tinyatoxin</td>
<td><sup id="cite_ref-24" class="reference">[24]</sup></td>
</tr><tr><td>15,000,000 to 16,000,000</td>
<td>Capsaicin,<span> </span>Dihydrocapsaicin</td>
<td><sup id="cite_ref-Govindarajan_Sathyanarayana_1991_25-0" class="reference">[25]</sup><sup id="cite_ref-:1_14-1" class="reference">[14]</sup></td>
</tr><tr><td>9,200,000</td>
<td>Nonivamide</td>
<td><sup id="cite_ref-Govindarajan_Sathyanarayana_1991_25-1" class="reference">[25]</sup></td>
</tr><tr><td>9,100,000</td>
<td>Nordihydrocapsaicin</td>
<td><sup id="cite_ref-Govindarajan_Sathyanarayana_1991_25-2" class="reference">[25]</sup><sup id="cite_ref-:1_14-2" class="reference">[14]</sup></td>
</tr><tr><td>8,600,000</td>
<td>Homocapsaicin,<span> </span>Homodihydrocapsaicin</td>
<td><sup id="cite_ref-Govindarajan_Sathyanarayana_1991_25-3" class="reference">[25]</sup></td>
</tr><tr><td>160,000</td>
<td>Shogaol</td>
<td><sup id="cite_ref-:0_26-0" class="reference">[26]</sup></td>
</tr><tr><td>100,000 to 200,000</td>
<td>Piperine</td>
<td><sup id="cite_ref-27" class="reference">[27]</sup></td>
</tr><tr><td>60,000</td>
<td>Gingerol</td>
<td><sup id="cite_ref-:0_26-1" class="reference">[26]</sup></td>
</tr><tr><td>16,000</td>
<td>Capsiate</td>
<td><sup class="noprint Inline-Template Template-Fact">[<i><span title="This claim needs references to reliable sources. (July 2019)">citation needed</span></i>]</sup></td>
</tr></tbody></table>